Learn the terminology of mushroom cultivation
Culture, spawn, grain, flush, pins. What does it all mean?
In the mushroom house's guide to the terminology in mushroom cultivation, you will learn all the terms that are good to know in order to understand and learn more about mushroom cultivation.
Historically speaking, mushroom cultivation has not taken place in Sweden on a large scale, with the exception of mushroom cultivation. Therefore, many foreign terms are used when talking about mushroom cultivation. In this list, we promise to teach you everything you need to know in order to understand what people mean in various mushroom growing forums.
Did we miss a term? Get in touch and we'll add more!
Mycelium - The vegetative part of the fungus that grows underground and consists of fine white "threads".
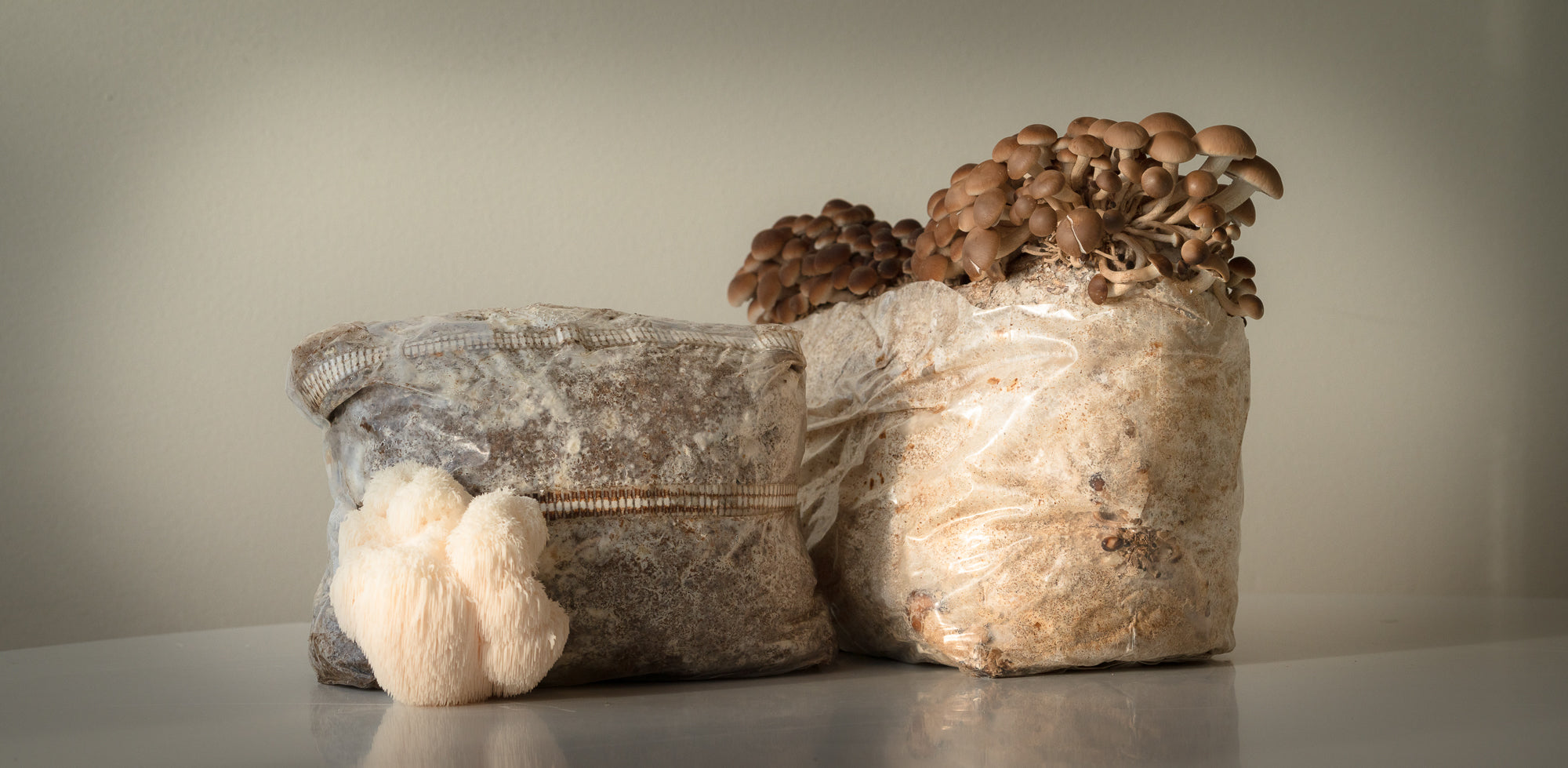
Cultivation - Another term for cultivating. In our case to grow mushrooms. It can be done both indoors or outdoors. Mushroom cultivation has four phases: inoculation, colonization, fruiting and harvesting.
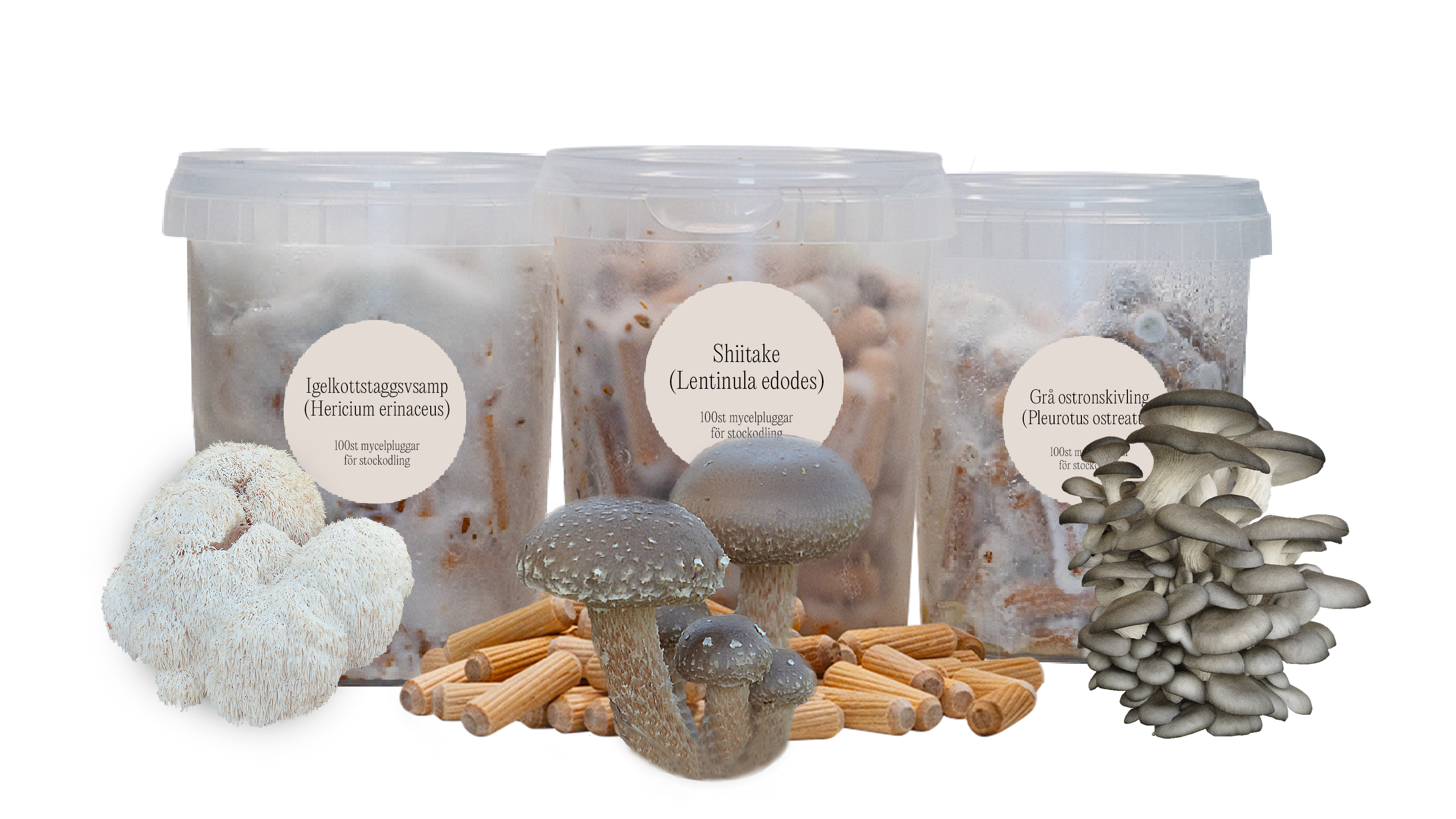
Inoculation - The process of introducing spores, liquid mycelium, mycelium from agar, mycelial plugs, fast growing mycelium or "spawn" into a substrate or log.
Colonization - When the mycelium grows, but no fruiting bodies (fungi) are present. Colonization can occur in Petri dishes with agar, liquid malt solutions, on grain (wheat, rye, straw pellets and other bulk substrates), outdoors or in logs. Actually, wherever the mycelium can grow, colonization can take place.
Culture or mother culture - Fungal mycelium of a particular species or strain, usually kept on a petri dish or inclined culture tube containing agar solution.
Cloning - Cloning fungal genetics into a culture. Can be done in different ways, but usually by taking a tissue sample from a fruiting body that is placed on agar in a petri dish. The mycelium will then grow out of the tissue sample by consuming the nutrients in the agar mixture in the petri dish and then be a clone of the fruiting body or tissue that has been grown.
Culture block - Substrate placed in a culture bag after inoculation of mycelium, full colonization has occurred. Typically, a growing block consists of various individual substrates with added grain. Common substrates used are straw pellets, oak pellets, grains such as rye and wheat and wood chips from hardwood trees.
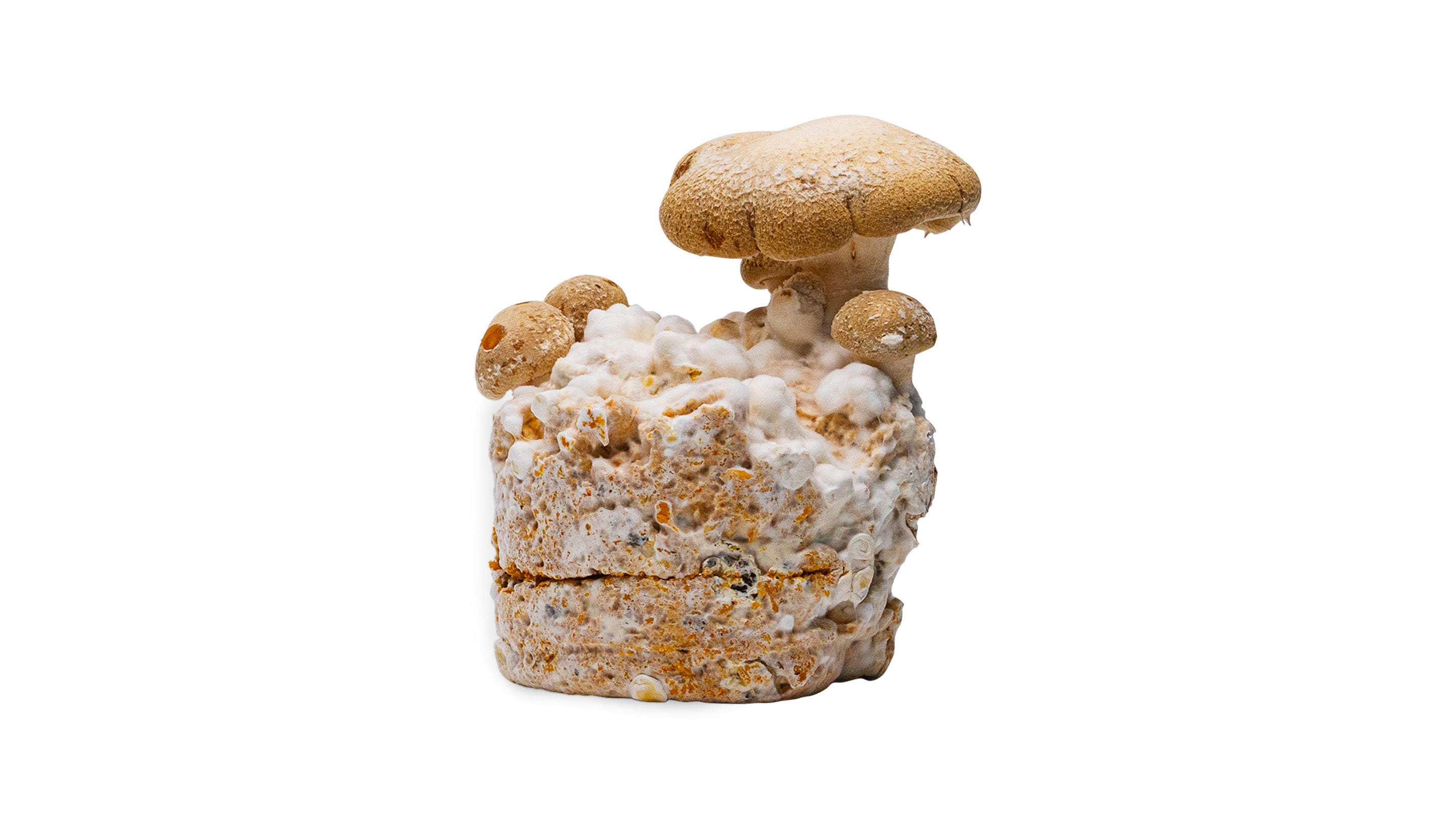
Flush - A harvest of mushrooms. Mycelium tends to produce fruit in groups, followed by a short period of rest. If you grow indoors in cultivation blocks, you usually get several "flushes", or harvests from one and the same cultivation. Outdoors, a flush usually occurs after rain, but is also determined by humidity and/or temperature.
Forced fruiting - A process used to trigger the mycelium to produce fruiting bodies. Also called "to shock".
Fruiting - The growth phase where visible fungi begin to appear on the substrate.
Fruit chamber - An enclosed space that is a mushroom grower's best friend. Used to create an optimal growing environment for best fruiting.
Laying site - The place where logs are incubated and routine maintenance is performed.
Primordia - Also called hyphal nodes. A stage where the hyphae of the mycelium bind together in preparation for fruiting.
Pins - When small fruiting bodies ( minimushrooms ) first start to appear.
Spawn - The colonized "carrier" that holds a specific strain of fungal mycelium until it is ready to transfer to another substrate. Spawn can, for example, be mycelium on sawdust, the mycelium on rye or the like. On grain it is called Grain Spawn, which is what mushroom growers usually use to inoculate growing substrates.
Spores - What fungi release into the air to reproduce. In the lab, you can use them to isolate specific fungal genes and create a mycelium.
Strain - A specific variety within a mushroom species.
Substrate - Any material on which fungus can grow.